
In simple terms, a substrate (Media/Accessory) is the layer on which printed images “stay.” It can be paper, plastic, metal, glass, or even fabric. The surface tension, smoothness, and ink absorption of the substrate directly affect how the ink droplets spread and cure.
If the surface is too smooth or has low surface energy, the ink may fail to adhere properly, leading to dropout, peeling, or color inconsistency. Therefore, selecting a substrate that matches the ink type is essential to ensure printing stability and color consistency.
PP is a non-polar material with extremely low surface energy. Its chemical stability and hydrophobic nature make it difficult for ink to wet and adhere. The surface is smooth with low friction, offering excellent chemical and heat resistance. Untreated PP sheets usually require corona or flame treatment to increase surface energy and improve ink adhesion.
PET is a polar material with relatively high surface energy. It provides excellent dimensional stability, rigidity, and tensile strength. Its high crystallinity and stable chemical structure allow it to withstand high temperatures without deformation. PET film offers a flat, dense surface that ensures stable ink adhesion, though prolonged exposure to high temperatures may cause warping.
PVC is a polar material with medium surface energy and features good flexibility and plasticity. The chlorine content provides chemical resistance and flame retardancy, but heating can release chlorides. Its fine surface texture and moderate roughness allow for mechanical bonding with inks, helping maintain strong adhesion.
Leather surfaces are porous and contain natural oils and unevenly distributed fibers. While highly absorbent, their surface flatness is poor. Different tanning processes affect the chemical stability and hydrophilicity of the leather. Natural leather may resist ink penetration and adhesion due to surface wax or oils.
Metals have very high surface energy and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. While smooth, they often oxidize, forming a thin layer that affects ink adhesion. The oxide layer’s thickness and surface roughness directly impact ink wetting and bonding. Some metals require surface treatment to stabilize adhesion.
Glass is a high surface energy material with a flat, chemically stable surface, but its non-porous structure makes ink penetration difficult. The silicon-oxygen surface has hydrophilic properties, but dust, oil films, or silicone residues can drastically reduce adhesion. Properly treated glass offers a stable and uniform surface for printing.
Fabric is soft, breathable, and absorbent, featuring an interwoven fiber structure that can hold dye molecules. Polyester fabrics are particularly compatible with sublimation inks—colors penetrate the fibers for rich, vivid, and wash-resistant results.
Different substrates require specific ink types to balance adhesion and color vibrancy. The table below summarizes common combinations and their typical applications.
| Substrate Type | Compatible Inks | Application Range |
|---|---|---|
| PP (Polypropylene) | Eco Solvent Inkjet Ink UV/LED UV Curing Ink Water Based Ink | Display boards, information signage |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Stickers, banners, wall graphics, exhibition prints, vehicle wraps | |
| PET | Eco Solvent Inkjet Ink UV/LED UV Curing Ink | Backlit films, transparent displays, nameplates, glass decals |
| Lightbox Film | Eco Solvent Inkjet Ink UV/LED UV Curing Ink Water Based Ink | Backlit signage, shopping mall displays, outdoor advertising |
| Metal (Aluminum, Stainless Steel) | Eco Solvent Inkjet Ink UV/LED UV Curing Ink Water Based Ink | Industrial nameplates, decorative panels, outdoor signs |
| Glass / Acrylic | Home décor panels, displays, advertising walls, art prints | |
| Fabric (Polyester, Flag Fabric) | Sublimation ink Eco Solvent Inkjet Ink | Exhibition backdrops, flags, hanging banners, soft signage |
When selecting inks, consider not only adhesion but also sustainability and durability. For instance, UV/LED UV Curing Ink require no solvent evaporation and emit minimal VOCs, aligning with green printing standards.
Some substrates are inexpensive and smooth but have poor ink adhesion. In such cases, Corona Treatment or Coating Application can be used to increase surface energy, allowing ink droplets to spread evenly.
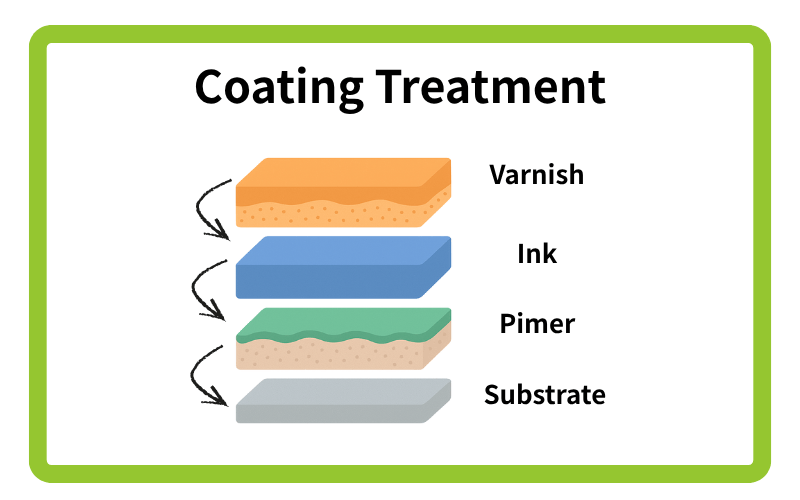
In actual print structures, some substrates include a coating layer to improve ink absorption and color vibrancy. The ink layer is then printed on top, forming the primary image. For environments requiring durability or weather resistance, a varnish or overcoat may be applied to enhance scratch resistance and longevity.
For glass or metal materials, applying a special primer before printing can significantly improve adhesion and abrasion resistance.
Choosing the right substrate allows colors to appear more vibrant and images to last longer. Whether for high-end industrial printing or creative advertising output, understanding substrate characteristics and ink compatibility is the first step toward achieving both quality and sustainability.
As green printing and smart manufacturing evolve, adopting high-compatibility, low-VOC, and sustainable printing substrates will be key to advancing the print industry toward premium quality and environmental responsibility.